So, fundamental to many electronic projects is switching. Also, switching is where a MOSFET can really shine. Why? Because most have a low on resistance and require voltage to turn on. Also, for this I am focusing on enhancement mode MOSFET’s. Also, focusing on DC at this point as AC has its own set of requirements and should be handled with a triac if true AC wave is zero crossing.
Types of Switching
High Side
High Side switching is turning off the input voltage and current above the load. So, this is like a typical switch application. Simply put, the switch is above the load or Hot side of the load. Controlling this way has its logical advantages. For example, where a load is going to have a common ground.


Low Side
Low side is often preferred if it is possible be done. Here are the main reasons.
- Typically, Less components.
- More efficient
- Better power handling.
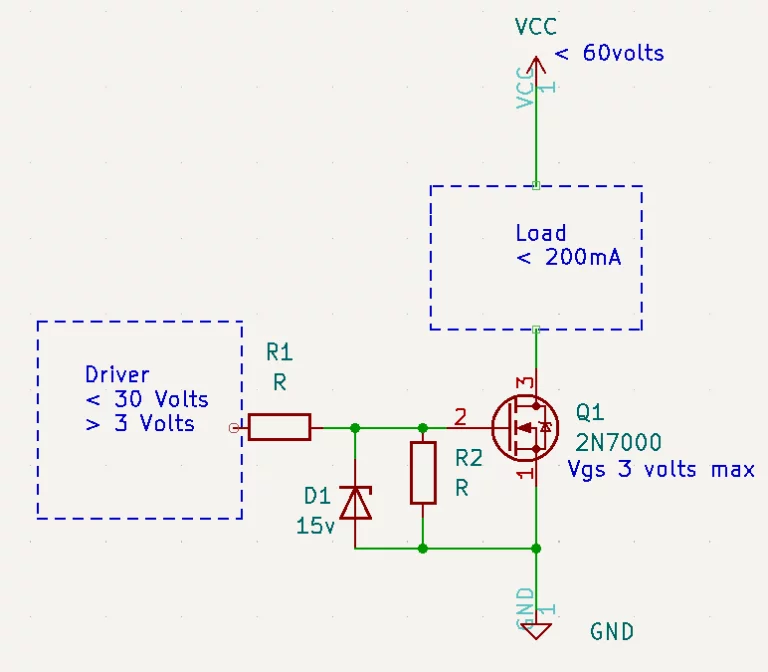
So, the first one is obvious. Now, remember the MOSFET is voltage controlled so if controlled via a micro controller it is important to note Vgs has to be low enough to fully activate the MOSFET to achieve the Rds that it is capable of driving. In other words, find a Vgs that is about 10 to 50 percent lower than Vgs on. Also, make sure not to exceed the maximum Vgs as well. If needed a Zenor can be added between gate and ground as shown in example 2 below.



Ahaa, its pleasant discussion concerning this article at this place at this webpage, I have read all that, so at this time me also commenting at this place.